Flow Cytometry Unit
Flow cytometry is a technique that allows the analysis of the physical and/or chemical characteristics of living cells and other biological particles. This technique is based on suspending the cells in a stream of fluid and passing one by one through a focalized laser beam. The impact of each cell with the beam of light produces signals corresponding to different parameters of cells which are collected by different detectors. These parameters provide information about cellular properties such as size and complexity. And, if the particle is stained with one or more fluorescent molecules, it will provide additional biological information when excited. The emitted light signals are converted to electronic pulses that can be processed by the computer.
The development of Cytometry comes together with early advances in microscopy. The first investigations were the UV light source on samples. However, it was in 1934 that the first technique for counting cells flowing through a capillary tube was described, and then flow cytometry was born. In 1880 fluorochromes were used for the first time; but it was not until 1960-70 that they were applied to cytometry to measure DNA cell content immunophenotyping. Over time, cell separation was firstly associated with cytometry. Los Alamos National Laboratories (USA) developed the first cell counter able to measure the presence of cells and to separate them into droplets and charge them. Cell sorters have the same performances and possibilities than flow cytometers; however, cell sorters present the additional capacity to separate (sorting) and recuperate particles selectively from the liquid suspension according to their characteristics.
The Flow Cytometry and Sorting Unit of GENYO is dedicated to the application and development of different techniques aimed at detecting the characteristics of biological particles through cytometry and cell sorting techniques, in order to provide to the users the state-of-the-art biomedical research.
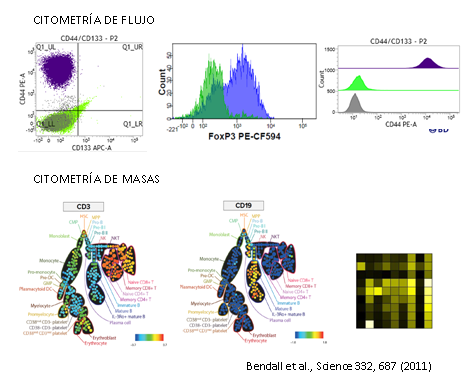
Estas limitaciones llevaron a la búsqueda de nuevas soluciones capaces de medir de forma simultánea en una única célula multitud de parámetros. De esta forma apareció la CITOMETRÍA DE MASAS, donde se combinan dos grandes tecnologías bien establecidas como son la citometría de flujo y la espectrometría de masas.
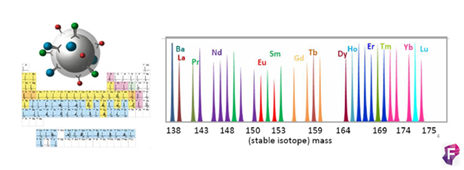
Este método ofrece la posibilidad de analizar de forma simultánea más de 35 parámetros sin problemas de superposición entre espectros y disminuyendo el ruido de fondo. El Dr. Sean C. Bendall y sus colaboradores fueron los pioneros, ellos en vez de usar moléculas fluorescentes usaron isotipos estables de elementos químicos pesados (metales de transición y lantánidos) para marcar los anticuerpos. Hay un total de aproximadamente 50 elementos disponibles.
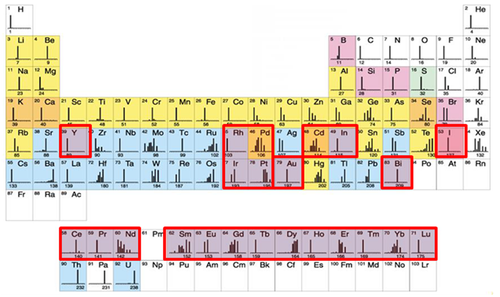
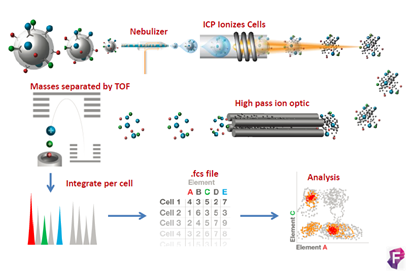
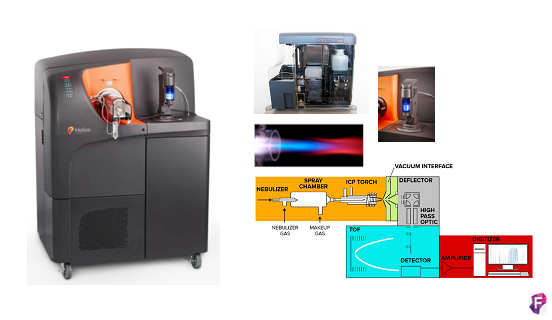
Como la principal diferencia entre cada uno de estos elementos es su masa atómica, los podemos discriminar en base a su peso. El único equipo que puede hacer este trabajo es el espectrómetro de masas con un analizador de tiempo de vuelo (TOF-MS).
El fundamento de la técnica es el siguiente las células son marcadas en suspensión con un panel diseñado de metales pesados conjugados con anticuerpos frente a dianas en la superficie y en el interior de las células, la técnica es muy similar a la citometría de flujo convencional. La alta pureza de los isotopos metálicos asegura un nivel muy bajo de background por solapamiento entre señales o por componentes celulares endógenos. En el interior de Helios las células son atomizadas individualmente para quedarnos solo con los iones metálicos. Los iones procedentes de cada célula marcada forman nubes aisladas de iones. Los metales iónicos son medidos en la cámara Time-Of-Flight (TOF) y en función de su carga y masa (m/z) tendrán diferentes tiempos de vuelo antes de llegar al detector, los cuales serán únicos y específicos. Finalmente, el detector produce un espectro de masas donde identifica y representa la cantidad de cada isotipo metálico marcado por célula. Los datos se obtienen en formato .fcs y se pueden analizar en software de análisis convencionales o específicos para muestras multiparamétricas.
Mission
The main task of the Flow Cytometry and Sorting Unit of GENYO is to provide technical support on cytometry to the research groups of the Center and to other entities outside the Center.
Thanks to our state-of-the-art equipment and the large experience of the scientific and technical staff of our Unit, it is possible to develop the applications required by the users. Therefore, it is possible to achieve one of the priorities of GENYO, that is to integrate the applied, translational, and basic investigation, minimizing the transition between the development of new technologies, products, and procedures, and their application in the field of health.
Also, the goal of the technical equipment of the Unit is to ease the generation of new systems for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases associated to the human genetic variability by the application of new technologies, in order to obtain a research of excellence in the area of oncology and genomics applied to the health sector.
The main activity of the Unit is the analysis through flow cytometry and cell sorting thechniques. Therefore, we are able to detect the presence of molecules of interests by immunofluorescence techniques, fluorescent sensors, and fluorescent proteins fusion in fixed particles and living cells; this enables us to study cell dynamic processes. Another activity of the Unit is cell separation by sorting, which allows rapid and easy isolation of specific cell populations for their subsequent culture, genomic and proteomic study
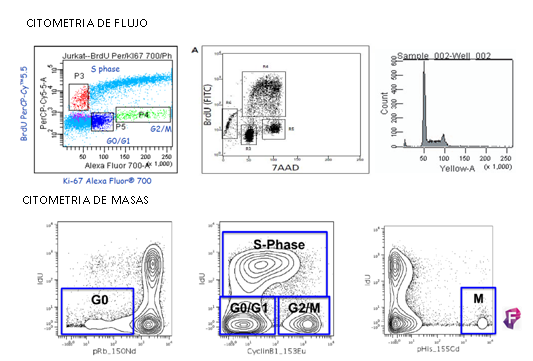
Análisis mediante citometría de masas
CyTOF®2 mejorado a Helios (DVS Sciences, Fluidigm), es un sistema de CyTOF® (Cytometry by Time of Flight), que incluye los más recientes avances en citometría de masas y está diseñado para ser una herramienta innovadora en la detección y análisis bionalítico a nivel de célula individual. El sistema se basa en la tecnología de espectrometría de masas en TOF con plasma acoplado inductivamente (ICP-TOF-MS), este nos permite analizar muestras unidas a isotopos de metales pesados, evitando el problema de la superposición de espectros y background que tenemos en la citometría de flujo convencional. Actualmente hay disponibles más de 40 marcadores para poder combinar. Como resultado obtenemos una gran resolución en los 135 canales de detección de los que dispone el sistema, permitiendo resolver de forma simultánea múltiples pruebas a velocidades altas, maximizando la información obtenida por célula en una única muestra.
La aplicación de esta tecnología hace que entendamos el organismo como un sistema de gran heterogeneidad celular, por ello la citometría de masas nos permite analizar marcadores tanto en el interior como en el exterior de la célula, dándonos una visión de su amplitud y complejidad, permitiendo una compresión a nivel de sistema y funcionalidad, con la resolución de célula única.
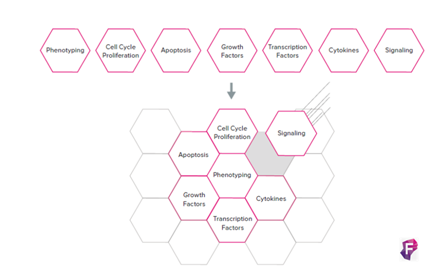
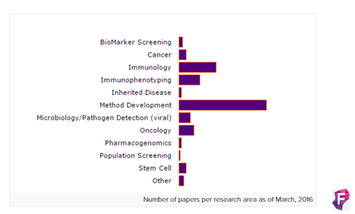
Las áreas de aplicación de esta innovadora tecnología incluyen desde cáncer, inmunología, inmunofenotipaje, enfermedades genéticas, screening de biomarcadores, metodología del desarrollo, detección en microbiología y patógenos (viral), oncología, farmacogenética y Stem Cell.
El sistema de trabajo con Helios es el siguiente:
DISEÑO: El método para el diseño de tu experimento es muy similar al de citometría de flujo convencional. Además, existe un programa que facilita la creación de los paneles https://www.fluidigm.com/paneldsigner.
CONSTRUCCIÓN: Existen en el mercado más de 400 anticuerpos conjugados con metales pesados para diferentes aplicaciones, tanto para humanos como para ratón. Además, kits que te permiten unir el anticuerpo de interés al metal pesado. También se existe la posibilidad de utilizar un sistema de Barcoding que permite analizar varias muestras juntas.
http://maxpar.fluidigm.com/product-catalog-metal.php
http://maxpar.fluidigm.com/product-catalog-panel-kits.php
http://maxpar.fluidigm.com/product-catalog-maxpar.php
http://maxpar.fluidigm.com/product-catalog-multi-metal-kits.php
http://maxpar.fluidigm.com/product-catalog-cell-id.php
http://www.biolegend.com/maxpar_ready
http://www.ebioscience.com/application/flow-cytometry/cytof.htm
https://www.fluidigm.com/singlearticles/how-barcoding-works
MARCAJE: El sistema es rápido sencillo, muy parecido al realizado con fluorocromos. Las células en suspensión son también marcadas en tubos con un panel de anticuerpos frente a la proteína de interés. Es muy importante utilizar buffers libres de metales. El último paso del protocolo incluye un intercalante del acido nucleíco utilizado para identificar eventos. Existen varios protocolos generales ya validados para el marcaje de los tres compartimentos celulares (superficie, citoplasma y núcleo) https://www.fluidigm.com/productsupport/cytof-helios. Las muestras pueden ser marcadas y enviadas para su posterior análisis.
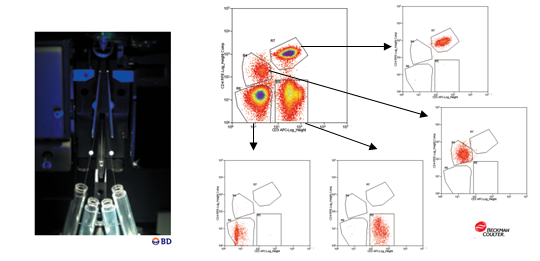
ADQUISICIÓN: La adquisición en Helios se realiza mediante un sistema de adquisición automático. Esta nueva versión del equipo, comparado con otras versiones, ahorra tiempo y facilita la introducción de la muestra. Además el software es intuitivo, con calibración automática, que permite mantener la calidad durante la adquisición.
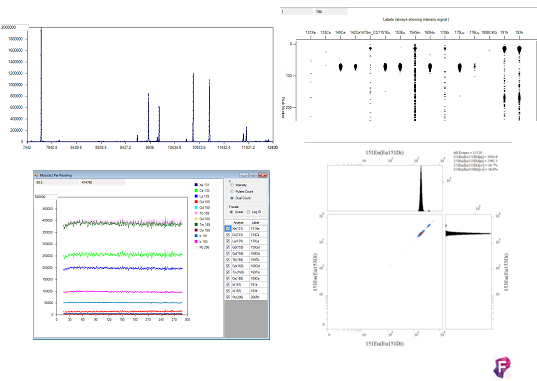
ANÁLISIS: El sistema genera archivos con formato .fcs que pueden ser analizados en software para citometría convencionales y/o específicos para este tipo de sistemas complejos. (http://fluidigm.cytobank.org/).
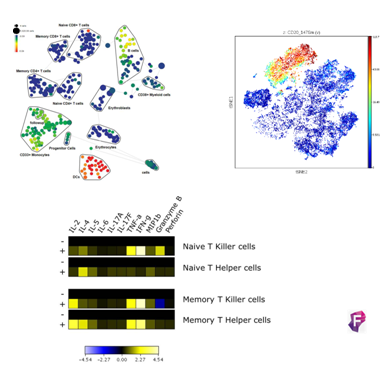
Flow Cytometry Analysis
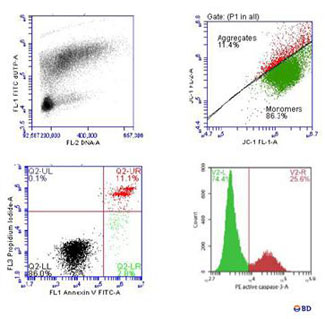
Cytometry uses one or more laser beams as excitation source. The beams enter into a biological particle that passes through the interrogation point. It allows to obtain rapidly and quantitatively the simultaneous measurement of multiple parameters of each biological particle. This system provides information about the complexity and size of the particle. Also, if the particle has been marked with fluorochromes, we can obtain additional information about the metabolic activity, DNA content, and presence of intra-and extra-cellular markers.
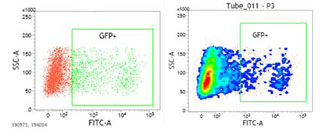
The sensibility of the state-of-the-art equipment of the Unit enables the detection of extremely rare cell populations, such as Stem cells, dendritic cells, antigen specific T-cells, or genetic transfections. In our Center, the most traditional applications of cytometry are based on cellular differentiation, immunology, and pathology, working with primary cells and cellular lines; the work of the Center is also based on the detection of reporter gene expression such as GFP, allowing the monitoring of gene transfection and the efficiency in protein expression levels. It also enables the user to perform assays which provide information about molecular interactions, protein structure, and DNA sequence. This technique allows to detect the binding of proteins to a target molecule in vitro, as well as to know the modulation of a signal of intracellular translation or identify specific proteins with binding, enzymatic activity, and protein expression level.
Although the research lines of GENYO are focused on clinical application and biomedical basic research, it is also possible to use cytometry technique in other fields such as environment where cytology is used for the study of unicellular organisms, in situ toxicity, or genomic analysis of cells of superior or inferior organisms.
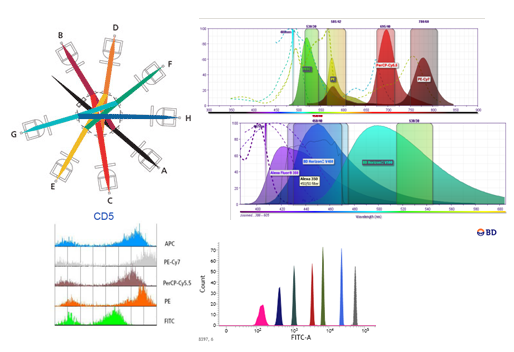
Cell Sorting
Cell separation by flow cytometry or “Cell Sorting” is a process for the physical separation of particles based on the differential expression of one or several parameters analyzed by analytical flow cytometry. It should be emphasized the great potential of multiparametric analysis in the identification of highly specific populations. Separation of cells or homogeneous cell populations are performed for subsequent biochemical, molecular, or cell differentiation assays of populations of interests; to that, sophisticated flow cytometry equipment, called cell sorter, is required. Cell Sorters are characterized by the capacity to obtain a high percentage of selected particles in the collection tube, from the total number of particles activated by the sorter, with a high purity, that is the percentage of sorted particles collected meeting the selected criteria according to the total particles analyzed. The cells exhibiting a special activity can be collected in a tube, plates, or microscope slides, with a purity of almost 99%. These particles preserve their features, including cell viability, to be used in subsequent studies.
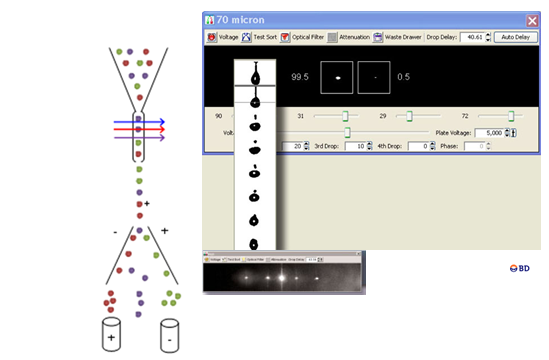
Particles separation or isolation can be very valuable in the isolation of specific cell populations in aseptic conditions to:
The Unit of Cytometry of GENYO has available the following equipment to support scientific community and develop the type of research studies described above:
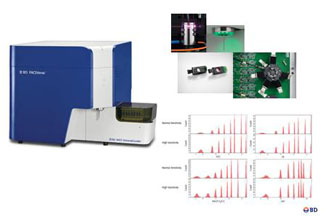
Citómetro de masas CyTOF®2 upgrade to Helios
Fabricante: DVS Sciences (Fluidigm)
Características técnicas:
El sistema se basa en la tecnología de espectrometría de masas de Time-Of-Flight con plasma acoplado inductivamente (ICP-TOF-MS), este nos permite analizar muestras unidas a isotopos de metales pesados. Presenta un sistema de introducción automática de las muestras que aumenta la eficiencia en un 60% con respecto a versiones anteriores y podemos recolectar más datos en menos tiempo y con menos muestra. Además, permite adquirir hasta 5 ml de muestra lo que permite trabajar más fácilmente con barcoding, permitiendo adquirir todo el experimento sin necesidad de ir introduciendo muestras secuencialmente. El sistema de agitación elimina el problema de sedimentación. Se elimina el uso de jeringas para introducir la muestra y de solución transportadora, que hace diluir la muestra, es su caso se utiliza el argón. Tiene un nuevo inyector de muestra transformado que hace que la nube de iones procedentes de cada células sea la mitad de grande (aprox. 1mm) que las de CyTOF 1 y 2. Además, un amplificador de señal modificado que conserva el rango dinámico necesario por la señal necesitando menos señales por pulso, en definitiva, menos pulsos para detectar la señal, por lo que detecta más señales con menos ruido de fondo. Debido a estos dos cambios se dobla el número de células que pueden resolverse por unidad de tiempo. Helios escribe cuatro nuevos parámetros Gaussianos para discriminación en las fcs files: anchura, residual, centro y offset. Estos parámetros están pensados para diferenciar eventos de iones fusionados de los simples.
En general las características principales son:
BD FACTSCanto II Flow Cytometer
Trademark: BD Biosciences
Technical Specifications: Technical Specifications: It is equipped with a solid state Coherent® Sapphire™ air-cooled blue laser (488-nm, 20-mW) able to detect 4 colors; JDS Uniphase™ HeNe (633 nm y 17 mW) red laser with 2 colors. It is equipped with a total of 8 detectors (6 fluorescence detectors and 2 morphologic parameters). It runs with the FACSDiva software. The system is equipped with a module of quality control that determines the optimal voltages and checks the system for best performance.

BD FACSVerse™ Flow Cytometer
Trademark: BD Biosciences
Technical Specifications: It is used in investigation. It is provided with three laser lines: blue laser (488-nm) for 4 colors, a red laser (633nm) for 2 colors, and a violet laser (407nm) for 2 colors. It is able to detect up to 10 dispersion parameters (8 fluorescence detectors and 2 morphologic parameters). It presents a laser system designed to minimize light losses and maximize resolution for multiparametric applications. It has a micro motor for automated laser alignment. This cytometer presents standard acquisition velocity rates (high, medium, and low), and a high-sensitivity mode making easier the detection of dimly staining particles. The fluidic system allows handling acquisition of samples in any tube format. It has a sample loader able to analyze from 30-40 tubes in a single run to 96 and 384 well-plates. It has volumetric counting. It runs with the FACSuite software. The system is equipped with a module of quality control that determines the optimal voltages and checks the system for best performance to maximize reliability of results.
BD FACSAria Cell Sorter
Trademark: BD Bioscencies
Technical Specifications: : It is provided with three laser lines: The Coherent ® Sapphire ™ solid state blue laser (488 nm, 13 mW) can detect 5 colors; The Coherent Sapphire diode-pumped solid-state blue laser (488 nm, 13 mW) is able to detect 5 colors; JDS Uniphase™ air-cooled HeNe (633 nm y 17 mW) red laser for 2 colors (633 nm, 11mW), and solid-state violet laser (407 nm and 10 mW) for 2 colors. It is able to detect up to 11 dispersion parameters simultaneously (9 fluorescence detectors, Forward Scatter (FSC) and Side scatter (SSC)), as well as to purify different types of cell populations based on specific features. Acquisition velocity rate can reach up to 70,000 events per second. It accepts different supports for samples acquisition and sorting. It is equipped with ACDU (Automated Cell Deposition Unit) Unit for sorting into multi-well plates or slides. The FACSAria is equipped with a refrigeration system that allows samples acquisition and sorting with controlled temperature. It runs with the FACSuite software for sample acquisition and analysis.

List of Services
Links
Area Coordinator:
Concepción Marañón Lizana
Technical manager:
Olivia Santiago Puertas
Technician:
Fernando Barba Pareja
Jose Francisco Díaz Cuellar



 Intranet
Intranet